Explore the real difference between DOM and Virtual DOM in JavaScript with real-life examples, performance benchmarks and best practices for modern frontend development.
DOM vs Virtual DOM in JavaScript – What's the Real Difference?
If you've been building websites or web apps with JavaScript or frameworks like React, you've likely come across the terms DOM and Virtual DOM. While they may sound technical and abstract, these concepts directly affect the speed, performance and responsiveness of your website.
In this blog post, we’ll break down:
• What is the DOM in JavaScript?
• What is the Virtual DOM?
• How do they differ in performance?
• Which one is faster and why?
• Real code examples to better understand
What is the DOM?
The DOM (Document Object Model) is an interface that represents the structure of an HTML document as a tree of nodes. You can manipulate the DOM using JavaScript to change text, styles, elements etc.
Example:
The Real DOM is:
• A real object in memory
• Slow to manipulate when the page has many elements
• Causes reflows and repaints on updates
What is the Virtual DOM?
The Virtual DOM is a lightweight, in-memory representation of the real DOM. It's used by libraries like React to increase performance.
Instead of updating the real DOM directly, frameworks first update the Virtual DOM, then compare it with the previous version using a diffing algorithm and finally update only the necessary parts in the real DOM.
React Example:
Virtual DOM:
• Improves performance
• Only updates changed elements
• Reduces unnecessary DOM operations
DOM vs Virtual DOM – Key Differences
| Feature | Real DOM | Virtual DOM |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Actual interface | Abstract representation |
| Performance | Slower with large updates | Faster with optimized diffing |
| Manipulation | Directly via JS | Updated in memory first |
| Reflow/Repaint | More frequent | Reduced with batching |
| Framework Usage | Vanilla JS, jQuery | React, Vue, Svelte (with variations) |
Performance Benchmark
Updating 1000 DOM nodes:
• Real DOM: Repaints the whole tree
• Virtual DOM: Updates only the node that changed
This is why React and Vue are so fast compared to plain JavaScript or jQuery.
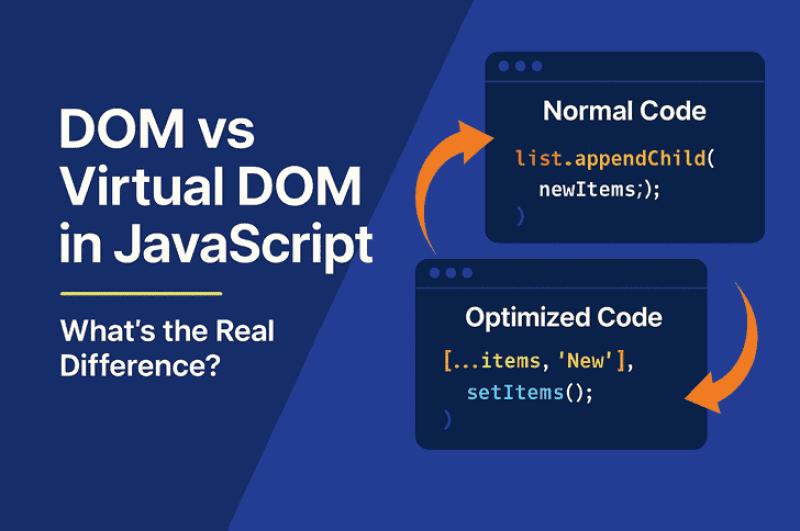
Source Code Comparison
🔴 Without Virtual DOM (Vanilla JavaScript)
🟢 With Virtual DOM (React)
When to Use Which?
| Situation | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Small projects or simple sites | Real DOM (Vanilla JS / jQuery) |
| Large, dynamic web apps | Virtual DOM (React / Vue) |
| Performance-critical UIs | Virtual DOM |
| Direct element control needed | Real DOM |
The Virtual DOM is not a replacement for the real DOM — it's a smart optimization layer that makes our applications faster and more efficient. Whether you choose to use the real DOM directly or rely on frameworks with Virtual DOM depends on your project size, performance needs and personal preference.